Genre: eLearning | MP4 | Video: h264, 1280x720 | Audio: aac, 44100 Hz
Language: English | VTT | Size: 2.57 GB | Duration: 3 section | 7 lectures | (5h 9m)
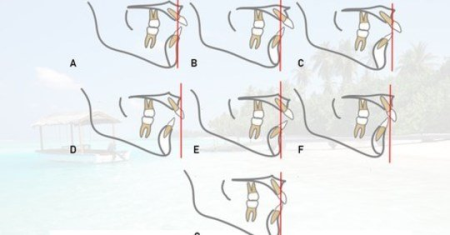
Development of crossbite.
What you'll learn
Transverse discrepancies
Types of posterior cross bites. Disjunction. Treatment for posterior cross bite
Treatment of sagittal discrepancies. Class II malocclusion. Treatment planning. Dentoalveolar Class II malocclusions.
Maxillary distalization. Functional Class II with distally forced bite. Skeletal Class II with maxillary prognathism.
Extraction treatment. Skeletal Class II with prognathism and anteinclination of maxilla. Skeletal Class II with retrognathic mandible.
Class III malocclusion
Requirements
Interested in becoming an orthodontic specialist
Description
This course will take you from zero to hero of the following orthodontic topics: Transverse discrepancies and Treatment of sagittal discrepancies
Here are the main headlines that this course covers:
Transverse discrepancies
1. Development of crossbite
1.1 Classification
2. Posterior crossbite
2.1 Etiology of posterior crossbites
2.1.1Genetic factors
2.1.2 Habits
Mouth breathing
Finger sucking
Infantile deglutition
Lingual interposition
2.1.3 Interferences and occlusal factors
Trauma
Other causes
2.2 Types of posterior crossbites
Functional crossbite
Dentoalveolar crossbite
Skeletal crossbite
Scissors bite
2.3 Diagnosis for posterior crossbite
2.4 Variables that can have influence in the correction of posterior crossbites
Teeth inclination
Lateral functional displacement during mandible closure
Estimation of the necessary expansion
Age of the patient
Vertical changes
2.5 Reasons and timing of treatment of posterior crossbites
3 Disjunction
3.1 Effects of disjunction
3.2 Effects on the maxillary complex
3.3 Effects on the alveolar process
3.4 Dental effects
3.5 Effects on the mandible
3.6 Effects on the adjacent facial structures
3.7 Disjunction indications and Counter indications
4. Treatment for posterior crossbite
Quad Helix
Transpalatal arch with an extension arm
Inverted NiTi arch
Overlay
Crossed elastics or "Z" elastics
Hass
Hyrax
Sual disjunction
Treatment of sagittal discrepancies
1. Development of a sagittal problem
2. Diagnosis of sagittal discrepancies
3. Class II malocclusion
3.1 Clinical examination and functional assessment
3.2 Morphologic characteristics
3.3 Treatment planning
3.3.1 Dentoalveolar Class II malocclusions
Maxillary distalization:
Fixed distalizers - open coil spring, elastic NiTi wires or Dr Richard Vlock's technique, sliding hooks, Pendulum appliance, Distal jet
Removable distalizers - Cetlin plate, Veltri distalizer, Belussi Distalizer
Non extraction headgear treatment
3.3.2 Functional Class II with distally forced bite
3.3.3 Skeletal Class II with maxillary prognathism
Extraction treatment
Management of the extraction space
Indications and contraindications
Extraction pattern in class II cases
Extraction space closure biomechanics by:
1. Elastics,
2. Coils,
3. Loops:
The open ''I'' loop.
The closed ''I'' loop.
The closed helicoid ''I'' loop,
Ricketts loop.
Bull or Keyhole loop,
The "T" loop,
The snted "T" loop,
The utility retraction loop.
The DKL (Double Key Loops).
4. Retroligature
3.3.4 Skeletal Class II with prognathism and anteinclination of maxilla
3.3.5 . Skeletal Class II with retrognathic mandible
4. Class III malocclusion
4.1Treatment Problems
4.2 Anterior crossbite
Etiology
Clinical evaluation
Classification - Dental anterior crossbite, Functional anterior crossbite, skeletal anterior crossbite
Differential diagnosis between true and Pseudo Class III malocclusion
Treatments for anterior crossbites
1. Dentoalveolar Class III
Extraction treatment
Forward arch
Bite block
Lingually placed bracket
2. Functional Class III malocclusion (with pseudo-forced bite or anterior displacement)
3. Class III malocclusion with retruded maxilla
Face mask treatment
Orthognathic surgery
4. Class III malocclusion with mandibular prognathism
Orthognathic surgery
5. Class III malocclusion with a combination of maxillary retrognathism and mandibular prognathism
Who this course is for:
General dentists and post-graduate students
Dental students
DOWNLOAD
uploadgig
https://uploadgig.com/file/download/c18a9Ee7776dacBD/eFlhUL54__Orthodonti.part1.rar
https://uploadgig.com/file/download/9819a6e892436b64/eFlhUL54__Orthodonti.part2.rar
https://uploadgig.com/file/download/5292Fcc890ce2d8b/eFlhUL54__Orthodonti.part3.rar
rapidgator
https://rapidgator.net/file/617c27fe322d0f16ab810853ad36bb2a/eFlhUL54__Orthodonti.part1.rar
https://rapidgator.net/file/97c64952f574af47951a4ae912048f0e/eFlhUL54__Orthodonti.part2.rar
https://rapidgator.net/file/fb3d9d1d272d86304bd1f9e06211c6ef/eFlhUL54__Orthodonti.part3.rar
nitroflare
http://nitroflare.com/view/A1FA6CFCF36A39F/eFlhUL54__Orthodonti.part1.rar
http://nitroflare.com/view/BAD01DCEE3C1CFB/eFlhUL54__Orthodonti.part2.rar
http://nitroflare.com/view/1E9622B3DB0E111/eFlhUL54__Orthodonti.part3.rar

